Navigating the Cloud Security Landscape
Protecting your cloud infrastructure and data is crucial. This listicle covers eight essential cloud security standards to help your organization build and maintain a secure cloud environment in 2025. Learn about key standards like ISO/IEC 27017, CSA CCM, NIST CSF 2.0, SOC 2, FedRAMP, PCI DSS Cloud Security Guidelines, ENISA Cloud Security Framework, and COBIT 2019, and understand how implementing these cloud security standards can enhance your security posture, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance. These frameworks provide best practices to address evolving cyber threats and build a resilient cloud infrastructure.
1. ISO/IEC 27017:2015 – Code of Practice for Information Security Controls for Cloud Services
In today’s interconnected world, cloud security is paramount, especially for businesses operating in the IN region. With increasing reliance on cloud services, establishing robust security measures is no longer optional but a necessity. ISO/IEC 27017:2015 emerges as a crucial cloud security standard, offering a comprehensive framework for organizations to secure their cloud environments effectively. This international standard provides guidelines specifically designed for information security controls within cloud services, building upon the foundation laid by ISO/IEC 27002.
ISO/IEC 27017 isn’t merely a theoretical document; it offers practical, actionable guidance for both cloud service providers and cloud service customers. It addresses the shared responsibility model inherent in cloud computing, clarifying the roles and responsibilities of each party in maintaining security. This is particularly important in the cloud context where responsibilities can sometimes be ambiguous. The standard delves into critical areas such as virtual network security, the security of the virtualization infrastructure itself, and, most importantly, the protection of customer data. It offers 37 cloud-specific security controls and provides implementation guidance for existing ISO 27002 controls adapted to cloud environments. This helps bridge the gap between general security best practices and the specific needs of cloud deployments.
Several features distinguish ISO/IEC 27017. It provides specific controls addressing cloud-unique risks like data location, segregation in virtualized environments, and recovery responsibilities. Its guidance on shared responsibility clarifies who is responsible for which security aspects, reducing ambiguity and potential security gaps. The standard’s alignment with the broader ISO 27000 series allows for seamless integration with existing information security management systems (ISMS).
The benefits of adopting ISO/IEC 27017 are numerous. Its international recognition and vendor neutrality assure organizations of its credibility and applicability across different cloud platforms. The comprehensive coverage of cloud-specific security concerns provides a strong defense against evolving cyber threats. Alignment with the ISO 27000 series streamlines compliance efforts and strengthens overall security posture. Furthermore, adherence to ISO/IEC 27017 can significantly assist organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements, demonstrating a commitment to data security and best practices. Real-world examples demonstrate the standard’s effectiveness. Microsoft Azure, AWS, and enterprise organizations like Siemens have adopted ISO/IEC 27017 to enhance their cloud security and governance, showcasing its practical application and value.
However, implementing ISO/IEC 27017 is not without its challenges. It can be a complex and resource-intensive undertaking, requiring significant expertise to interpret and apply effectively. The certification process can be lengthy and expensive, and the standard may not fully address the nuances of all emerging cloud technologies. Therefore, a phased approach, potentially with the help of certified consultants, is often advisable.
When considering ISO/IEC 27017, organizations should conduct a thorough gap analysis against their existing security practices. Engaging with cloud service providers who are already ISO/IEC 27017 certified can simplify implementation. Focusing on the shared responsibility model is crucial for clear delineation of security obligations. Integrating the standard with existing ISO 27001 management systems, if available, can create a more cohesive and efficient security framework.
For organizations looking to establish robust cloud security, especially startups and enterprises in the IN region, ISO/IEC 27017 deserves serious consideration. While the implementation requires dedicated effort, the benefits of enhanced security, regulatory compliance, and international recognition make it a valuable investment.
The infographic below visualizes the interplay of three key concepts within ISO/IEC 27017: ‘Shared Responsibility Model’, ‘Virtual Network Security’, and ‘Customer Data Protection’.
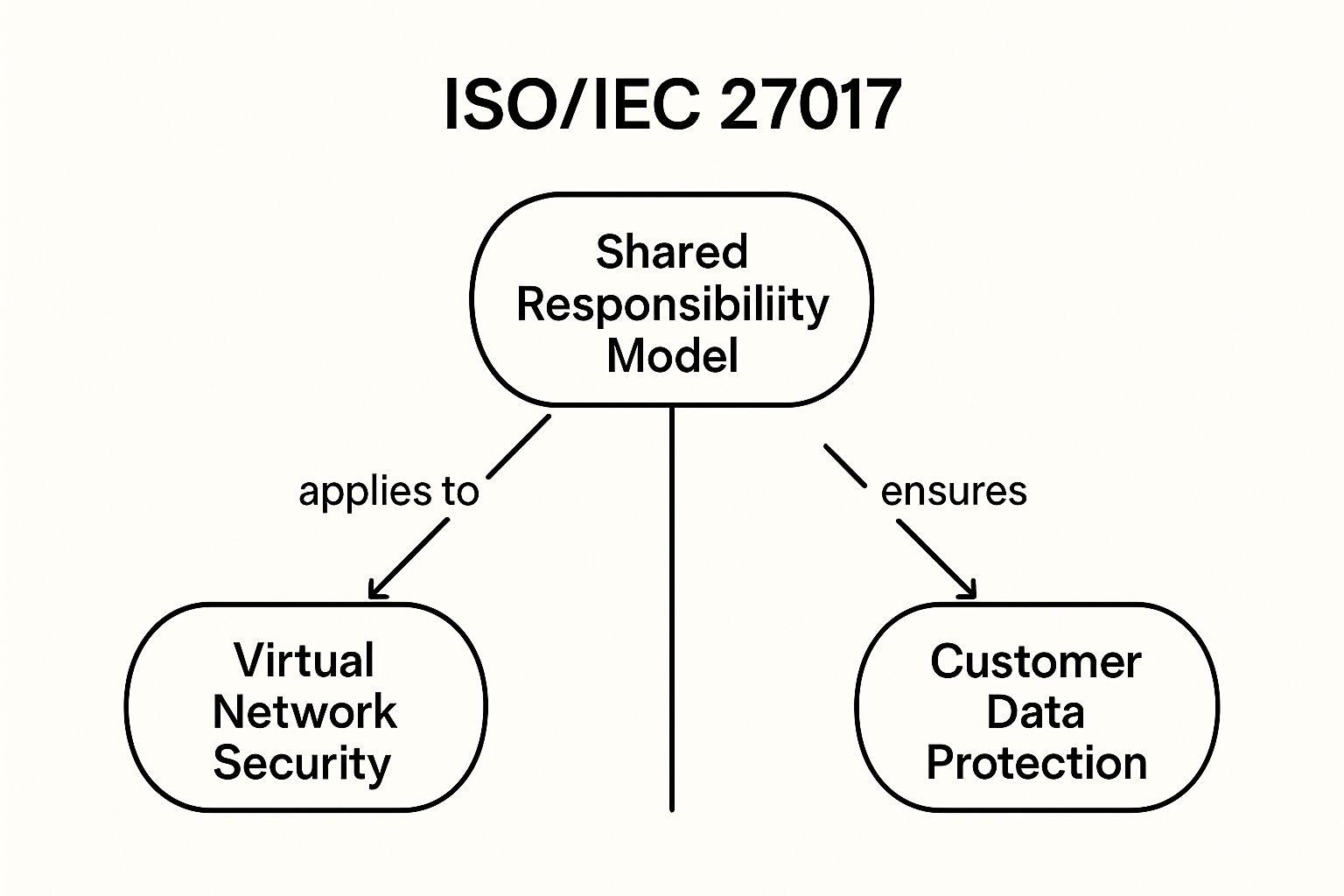
As the infographic illustrates, the Shared Responsibility Model serves as the central pillar, directly influencing both Virtual Network Security and Customer Data Protection. The visualization highlights how defining responsibilities within the Shared Responsibility Model is critical for securing the virtual network and protecting customer data effectively. This interconnectedness emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to cloud security, as weaknesses in one area can impact the others.
Starting with a gap analysis and focusing on the shared responsibility model are practical first steps toward implementing this standard. By leveraging the framework provided by ISO/IEC 27017, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of cloud security and protect their valuable assets in the digital landscape.
2. Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM)
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) stands as a leading cloud security standard, providing a comprehensive cybersecurity control framework specifically designed for cloud computing environments. It offers a detailed understanding of security concepts and principles aligned with the CSA’s extensive guidance across 17 different domains, enabling organizations to assess and enhance their cloud security posture effectively. The CCM acts as a structured blueprint, outlining specific control objectives that address various security risks and vulnerabilities inherent in cloud deployments. This framework is invaluable for startups, enterprises, and government agencies alike, offering a robust foundation for building and maintaining secure cloud infrastructures.

The CCM’s strength lies in its comprehensive coverage of 17 security domains, encompassing areas such as Application & Interface Security, Data Security and Privacy, Infrastructure & Virtualization Security, and more. With over 197 control objectives, the matrix maps to multiple established standards like ISO 27001/27002, NIST, and PCI DSS, streamlining compliance efforts. Its regular updates ensure that the framework stays current with emerging threats and evolving best practices in cloud security. The availability of the CCM in a machine-readable format further facilitates automation and integration with existing security tools and processes. The integrated Consensus Assessments Initiative Questionnaire (CAIQ) provides a standardized way to assess the security posture of cloud service providers, enabling informed decision-making and risk management.
The CSA CCM offers several compelling advantages. Developed by industry-leading cloud security experts, it represents a collective wisdom and best practices within the field. Its free and open availability makes it accessible to organizations of all sizes, fostering wider adoption and improved cloud security practices across the industry. The regular updates and alignment with multiple compliance frameworks ensure its relevance and practicality in addressing real-world security challenges. The CCM’s strong industry recognition and adoption provide further validation of its effectiveness as a leading cloud security standard.
However, the CCM’s comprehensiveness can also be overwhelming, particularly for organizations new to cloud security. Implementing the framework effectively requires expertise and a deep understanding of cloud security principles. It’s important to note that the CCM is not a formal certification standard, but rather a guidance framework. Some overlap with other security frameworks may also exist, requiring careful consideration and mapping to avoid redundancy.
Numerous successful implementations demonstrate the CCM’s practical value. Salesforce leverages the CCM for internal security assessments, while major cloud providers utilize it to enhance transparency and build trust with their customers. Financial services companies rely on the CCM to meet stringent regulatory compliance requirements, and government agencies adopt it for robust cloud security governance.
For organizations looking to leverage the CCM, several practical tips can facilitate effective implementation. Using the CAIQ to assess potential cloud service providers is a crucial first step. Mapping existing security controls to the CCM domains provides a clear picture of current strengths and weaknesses. Prioritizing implementation based on a thorough risk assessment ensures that resources are focused on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities. Leveraging the machine-readable format for automation streamlines security operations and enhances efficiency. Participating in CSA working groups provides access to the latest updates and best practices, keeping organizations at the forefront of cloud security. Learn more about Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM)
The CSA CCM earns its place among top cloud security standards due to its comprehensive nature, industry backing, and practical guidance. It is particularly relevant for organizations operating within the IN region, where the adoption of cloud computing is rapidly growing and robust security measures are paramount. By adopting and implementing the CCM, organizations can effectively manage cloud security risks, protect sensitive data, and build a strong foundation for secure and compliant cloud operations.
3. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 is a valuable resource for organizations seeking to bolster their cloud security posture. While not exclusively designed for cloud environments, the CSF offers a comprehensive, risk-based approach to cybersecurity that readily applies to the complexities of the cloud. It’s a crucial element in any discussion of cloud security standards due to its wide adoption and adaptable nature. Its inclusion in this list highlights its importance as a foundational framework for building robust cybersecurity programs, particularly relevant for organizations operating within the IN region or globally leveraging cloud services.
The CSF provides a flexible and adaptable set of guidelines rather than prescriptive rules. This framework functions around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. These functions represent the lifecycle of a cybersecurity incident and offer a structured approach to managing risks.
- Identify: This involves understanding your assets, systems, and data, as well as the associated risks and vulnerabilities. In a cloud context, this includes identifying all cloud resources, data storage locations, and access control mechanisms.
- Protect: This function focuses on implementing safeguards to limit or contain the impact of a cybersecurity event. For cloud security, this includes implementing strong access controls, data encryption, and network segmentation.
- Detect: This involves identifying the occurrence of a cybersecurity event. In the cloud, this translates to implementing security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and robust logging practices.
- Respond: This focuses on taking action to contain the impact of a detected cybersecurity incident. In cloud environments, this involves incident response plans, disaster recovery procedures, and business continuity strategies.
- Recover: This stage aims to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. For cloud deployments, this includes restoring data from backups, redeploying services, and ensuring business continuity.
The framework also defines three implementation tiers – Partial, Risk-Informed, and Adaptive – allowing organizations to tailor their approach based on their specific risk tolerance, resources, and business needs. Further enhancing its adaptability, the CSF offers framework profiles for customization and includes cloud-specific subcategories and informative references.
Why NIST CSF 2.0 for Cloud Security?
The CSF’s risk-based approach is particularly well-suited for cloud environments, where the shared responsibility model requires organizations to understand and manage their own security risks. By aligning with the CSF, organizations can effectively address the unique challenges presented by cloud adoption. Its voluntary and flexible nature means it can be integrated with existing security practices and adapted to evolving cloud deployments.
Benefits and Drawbacks:
The NIST CSF boasts several advantages, including its wide adoption across industries and government, risk-based and business-focused approach, and the fact that it’s free and publicly available. Its flexible design allows for adaptation to diverse organizational structures and its strong governmental backing ensures ongoing development and industry support with regular updates based on feedback.
However, the CSF isn’t without its limitations. It’s not specifically designed for cloud environments and its somewhat abstract nature can require interpretation and expert guidance for implementation. It’s important to remember that the CSF isn’t a compliance standard or certification in itself.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
The CSF is leveraged across various sectors. U.S. federal agencies are mandated to use it, while financial institutions utilize the CSF for risk management. Healthcare organizations often implement the CSF as part of their HIPAA compliance efforts, and critical infrastructure sectors are increasingly adopting it. Even cloud service providers themselves align their services with the CSF, demonstrating its broad applicability.
Actionable Tips for Implementing NIST CSF for Cloud Security:
- Start with a current state assessment: Use the framework to evaluate your existing security posture and identify gaps.
- Develop target profiles: Define your desired cybersecurity outcomes based on your business requirements and risk tolerance.
- Leverage informative references: The NIST website (https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework) provides valuable resources and implementation guidance.
- Integrate with existing risk management processes: Align the CSF with your current risk management framework for a cohesive approach.
- Consider cloud-specific subcategories: Pay close attention to the cloud-specific guidance provided within the framework for effective cloud deployments.
By following these tips and understanding the nuances of the NIST CSF, organizations of all sizes, from startups to enterprises, can significantly enhance their cloud security strategy. Whether you’re a cloud architect in India, a DevOps team lead, or a CTO making critical decisions, the NIST CSF provides a robust and adaptable framework to navigate the complex landscape of cloud security.
4. SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) is a crucial cloud security standard, especially relevant in today’s interconnected digital landscape. It acts as a rigorous auditing procedure designed to ensure that service providers securely manage data, protecting both the organization’s interests and the privacy of its clients. Developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), SOC 2 has become a hallmark of trust and reliability in the cloud service industry. This framework is particularly critical for companies operating in India, given the growing reliance on cloud services and the increasing importance of data privacy and security regulations like the upcoming Digital Personal Data Protection Bill.

SOC 2 operates on the basis of five trust service principles, providing a comprehensive framework for evaluating security posture. These principles are: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. These criteria encompass a wide range of controls relating to access control, system security, data encryption, incident response, and data privacy. The framework allows organizations to select the specific criteria relevant to their services, making it adaptable to various business models.
The SOC 2 audit process culminates in two types of reports: Type I and Type II. A Type I report assesses the design of security controls at a specific point in time, while a Type II report evaluates the operational effectiveness of these controls over a period, usually 6-12 months. This distinction is crucial for organizations seeking to demonstrate ongoing compliance and build stronger trust with their clients. The reports themselves are confidential and not publicly available, but organizations can provide assurance to clients and stakeholders that they have successfully completed a SOC 2 audit. This third-party attestation plays a significant role in differentiating organizations that prioritize security in a competitive market.
Numerous organizations have benefited from achieving SOC 2 compliance. Salesforce, Slack, Dropbox, Box, and countless other leading cloud service providers maintain SOC 2 compliance to meet the stringent security demands of enterprise customers. In India, with the increasing adoption of cloud services across sectors like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce, SOC 2 compliance is rapidly becoming a prerequisite for doing business, especially with larger enterprises and multinational corporations. Even infrastructure providers like AWS and Google Cloud undergo SOC 2 audits to demonstrate their commitment to security and data protection, further emphasizing the importance of this standard.
SOC 2 offers numerous advantages. It builds customer trust and confidence by providing independent verification of security practices. It can also serve as a competitive advantage, particularly when bidding for contracts with security-conscious clients. Furthermore, the comprehensive nature of the SOC 2 framework provides a robust structure for improving operational security.
However, obtaining and maintaining SOC 2 compliance is not without its challenges. The audit process can be expensive and time-consuming, requiring significant investment in resources and expertise. Organizations must commit to ongoing compliance and annual audits to maintain their certification. Implementing SOC 2 can also be complex, particularly for smaller organizations with limited resources. Learn more about SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) to understand the complexities and benefits further.
For organizations looking to achieve SOC 2 compliance, several actionable tips can streamline the process. Starting with a readiness assessment before the formal audit helps identify gaps and prioritize remediation efforts. Implementing continuous monitoring systems simplifies ongoing compliance and provides real-time visibility into security posture. Thorough documentation of security policies and procedures is critical for demonstrating compliance to auditors. Choosing experienced SOC 2 auditors familiar with your industry ensures a smooth and efficient audit process. Finally, leveraging automation tools for evidence collection can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in compliance. Plan for a 6-12 month timeline for achieving initial compliance, recognizing that ongoing maintenance and annual audits will be required to sustain certification. In conclusion, SOC 2 is a robust cloud security standard that demonstrates a commitment to data security and privacy, offering significant benefits to both service providers and their clients. It has rightfully earned its place among essential cloud security standards, particularly in the evolving digital landscape of India.
5. FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program)
FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program) stands as a critical cloud security standard, especially for organizations interacting with the U.S. federal government. It provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services, ensuring consistent security postures across federal agencies. This rigorous program plays a crucial role in the broader landscape of cloud security standards by providing a robust framework for securing sensitive government data. If your organization plans to offer cloud services to the U.S. federal government, understanding and complying with FedRAMP is not just recommended, it’s essential.
FedRAMP utilizes a “do once, use many” approach, meaning a single authorization can be leveraged by multiple agencies. This streamlined process allows federal agencies to rapidly adopt secure cloud technologies without conducting redundant security assessments, saving both time and resources. This system of authorization reuse is a key element of what makes FedRAMP so effective in promoting secure cloud adoption within the government.
How FedRAMP Works:
The FedRAMP process involves several key steps, including:
- Documentation: Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) must thoroughly document their system’s security controls, policies, and procedures, aligning them with NIST SP 800-53.
- Assessment: A Third-Party Assessment Organization (3PAO), accredited by FedRAMP, conducts a rigorous independent security assessment of the CSP’s cloud offering. This assessment validates the implementation of the required security controls.
- Authorization: Based on the 3PAO’s assessment, a federal agency or the Joint Authorization Board (JAB) grants an Authorization to Operate (ATO). The JAB provides Provisional Authorizations (PA) that are government-wide and accepted by all federal agencies. Individual agencies can also grant Agency Authorizations (AA).
- Continuous Monitoring: After authorization, CSPs must continuously monitor their systems for security compliance and report any incidents or changes to the authorizing agency. This ongoing monitoring ensures the continued security posture of the cloud environment.
FedRAMP Impact Levels:
FedRAMP defines three impact levels based on the potential impact of a security breach:
- Low: Applies to systems with the lowest potential impact on organizational operations and assets, individuals, other organizations, or the nation.
- Moderate: Applies to systems with moderate potential impact. The vast majority of federal cloud deployments fall under this category.
- High: Applies to systems where a security breach would have a severe or catastrophic impact on organizational operations, organizational assets, individuals, other organizations, or the nation. This impact level typically covers law enforcement, emergency services, financial markets, and other critical infrastructure.
Benefits of FedRAMP Compliance:
- Access to the Federal Market: FedRAMP authorization opens doors to a vast market of federal agencies seeking secure cloud solutions.
- Enhanced Credibility and Trust: Achieving FedRAMP compliance demonstrates a strong commitment to security, building trust with customers both inside and outside of the government.
- Standardized Security Posture: FedRAMP provides a standardized framework for cloud security, simplifying compliance and ensuring consistency across government agencies.
- Continuous Improvement: The continuous monitoring requirements of FedRAMP promote a culture of ongoing security improvement within organizations.
Challenges of FedRAMP Compliance:
- Cost and Resource Intensive: The FedRAMP process is notoriously complex and expensive, often exceeding $1 million in costs and requiring significant time and resources.
- Lengthy Authorization Timeline: Achieving FedRAMP authorization can take anywhere from 12 to 24 months, requiring careful planning and execution.
- Rigorous Requirements: The stringent requirements can be challenging for smaller companies and organizations with limited resources to meet.
Examples of Successful FedRAMP Implementations:
Major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Salesforce, and ServiceNow have achieved FedRAMP authorizations, demonstrating the feasibility of navigating the process for large organizations.
Tips for Achieving FedRAMP Compliance:
- Engage with FedRAMP PMO early: Early engagement with the FedRAMP Project Management Office (PMO) can help clarify requirements and streamline the authorization process.
- Hire experienced consultants and 3PAOs: Leveraging the expertise of experienced professionals is crucial for navigating the complexities of FedRAMP.
- Budget sufficient time and resources: Adequate budgeting for both time and financial resources is essential for successful FedRAMP implementation.
- Start with FedRAMP Ready designation: Achieving FedRAMP Ready status is a valuable stepping stone towards full authorization.
FedRAMP is a vital component of the cloud security landscape. While challenging, the benefits of achieving FedRAMP authorization, including access to a significant market and increased customer trust, make it a worthwhile investment for organizations aiming to serve the U.S. federal government. You can find more information on the official FedRAMP website.
6. PCI DSS Cloud Security Guidelines
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount for any business, especially when dealing with financial transactions. For organizations handling payment card information, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) serves as a vital set of security guidelines. While not solely a cloud security standard, PCI DSS provides crucial guidance for securing cardholder data within cloud environments, making it an essential consideration for businesses in the IN region and globally. Its comprehensive requirements and guidelines are designed to safeguard sensitive payment information and maintain customer trust. Therefore, it rightfully earns a place among the top cloud security standards.
PCI DSS adapts its 12 core requirements to address the specific challenges of cloud environments. These requirements encompass various aspects of security, including building and maintaining a secure network, protecting cardholder data, maintaining a vulnerability management program, implementing strong access control measures, regularly monitoring and testing networks, and maintaining an information security policy. The standard’s emphasis on cloud security is further reinforced by guidance on shared responsibility models, outlining the security responsibilities of both the cloud service provider and the client. This clarity helps organizations understand their roles in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
PCI DSS also includes specific requirements for cloud service providers regarding validation and attestation of compliance. This ensures that providers offering services to organizations handling payment card data meet the stringent security requirements of the standard. Tokenization and encryption requirements are also central to PCI DSS. These measures help protect sensitive cardholder data by replacing it with non-sensitive equivalents (tokens) and encrypting data in transit and at rest, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. Furthermore, the standard mandates network segmentation within cloud environments to isolate cardholder data environments and limit the impact of potential security breaches. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are also required to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities.
Benefits and Drawbacks of PCI DSS Compliance:
Implementing PCI DSS within a cloud environment offers several advantages. First and foremost, it is mandatory for any organization handling payment card data, ensuring a baseline level of security. The standard provides specific cloud guidance within an established framework, simplifying the process of building a secure cloud environment. Its strong focus on data protection builds customer trust and safeguards businesses from financial and reputational damage resulting from data breaches. PCI DSS enjoys industry-wide acceptance and recognition, making it a universally understood and respected security standard. Regular updates to the standard ensure it addresses emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Finally, the standard provides a clear compliance validation process, providing a structured approach to demonstrating adherence to its requirements.
However, achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance is not without its challenges. The compliance requirements can be complex and demanding, requiring significant resources and expertise. The validation and assessment process can be expensive, particularly for smaller organizations. Defining the scope of compliance can be tricky in dynamic cloud environments. The strict requirements of PCI DSS might also limit cloud service provider options, as not all providers meet the necessary criteria. Furthermore, compliance is an ongoing process, requiring continuous maintenance and updates.
Practical Examples and Implementation Tips:
Several real-world examples demonstrate successful PCI DSS implementation in cloud environments:
- E-commerce platforms using AWS or other cloud providers while maintaining full PCI DSS compliance.
- Payment processors leveraging cloud-based solutions to streamline operations while adhering to the standard.
- Retail companies migrating their Point-of-Sale (POS) systems to the cloud while ensuring secure payment processing.
- Financial institutions utilizing cloud infrastructure for payment processing within a PCI DSS compliant framework.
- SaaS payment solutions achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance to assure their clients of data security.
To successfully implement PCI DSS in a cloud environment, consider these actionable tips:
- Clearly define the scope of your cardholder data environment: Identify all systems, applications, and processes that handle sensitive payment information.
- Choose PCI DSS compliant cloud service providers: Ensure your chosen providers have undergone the necessary validation and attestation processes.
- Implement robust network segmentation: Isolate your cardholder data environment to limit the impact of potential breaches.
- Utilize tokenization to reduce the scope of compliance: Replace sensitive cardholder data with non-sensitive tokens wherever possible.
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing: Proactively identify and address security weaknesses.
- Maintain detailed documentation of all systems and processes: This is essential for audits and compliance validation.
PCI DSS is popularized and enforced by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) and endorsed by major payment card brands like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express. The payment processing industry as a whole relies heavily on this standard to ensure the security of cardholder data. While the PCI SSC website provides comprehensive resources, it’s advisable to consult with security experts experienced in PCI DSS compliance for tailored guidance specific to your organization’s needs. By prioritizing PCI DSS compliance, businesses in the IN region can demonstrate their commitment to data security, protect their customers, and solidify their reputation as trusted players in the digital economy.
7. ENISA Cloud Security Framework
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) Cloud Security Framework is a crucial standard for any organization operating within the EU, or handling data subject to EU regulations. It provides comprehensive guidance and recommendations on achieving robust cloud security, addressing both technical implementation and governance structures. Its inclusion in this list of top cloud security standards is warranted due to its strong focus on risk management, data privacy, and regulatory compliance within the European context. This makes it especially relevant for readers in the IN region working with European partners or clients.
The ENISA framework operates on a risk-based approach, encouraging organizations to identify and mitigate cloud-related risks based on their specific context. Instead of a one-size-fits-all solution, it promotes a tailored approach that considers the unique data protection needs, regulatory obligations, and operational requirements of each organization. This is essential because cloud security is not static; threats evolve, and regulatory landscapes shift. The framework’s emphasis on continuous risk assessment ensures organizations can adapt their security posture accordingly.
One of the key strengths of the ENISA framework lies in its alignment with specific EU regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive. For businesses handling personal data of EU citizens, adhering to GDPR is non-negotiable. The framework provides practical guidance on implementing technical and organizational measures to achieve GDPR compliance in cloud environments, covering aspects like data breach notification, data access controls, and data processing agreements. Learn more about ENISA Cloud Security Framework to understand how these principles can be integrated into your cloud architecture.
The ENISA framework adopts a multi-stakeholder perspective, recognizing the shared responsibility for cloud security across cloud service providers (CSPs), customers, and regulatory bodies. This collaborative approach fosters a more secure and transparent cloud ecosystem. For example, the framework encourages CSPs to provide clear and concise information about their security practices, enabling customers to make informed decisions when selecting a cloud provider. It also outlines incident reporting and handling procedures, facilitating effective communication and collaboration in the event of a security incident. Furthermore, the framework addresses the complexities of cross-border data transfers, a critical concern for multinational organizations operating in the EU.
Several benefits emerge from adopting the ENISA Cloud Security Framework:
- Tailored for the European Regulatory Environment: It simplifies compliance with complex EU regulations like GDPR and the NIS Directive.
- Strong Privacy and Data Protection Focus: It prioritizes data protection principles, essential for maintaining customer trust and avoiding costly fines.
- Government Backing and Authority: Backed by the EU, the framework carries weight and credibility, reinforcing the importance of cloud security.
- Comprehensive Risk Management Approach: It promotes a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating cloud security risks, improving overall resilience.
- Regular Updates: The framework is regularly updated to reflect the evolving threat landscape and regulatory changes, ensuring its ongoing relevance.
- Practical Implementation Guidance: It offers concrete advice and best practices that organizations can readily implement.
However, some potential drawbacks need consideration:
- Primarily Focused on the EU Market: While relevant for organizations operating within the EU, its applicability outside the EU may be limited.
- Potential Conflicts with Other International Standards: Alignment with other international standards requires careful consideration and potential reconciliation.
- Complex Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the complex EU regulatory landscape can be challenging, requiring specialized expertise.
- Resource-Intensive Implementation: Implementing the framework fully can require significant resources, especially for smaller organizations.
Examples of successful implementations include EU government agencies adopting cloud strategies based on the framework, European cloud service providers aligning their services with ENISA recommendations, and multinational companies operating in the EU using the framework to ensure GDPR compliance. Financial institutions and healthcare organizations also leverage the framework to meet specific regulatory requirements for data security and privacy.
For organizations looking to implement the ENISA framework, these tips can be helpful:
- Integrate GDPR Compliance from the Start: Embed data protection principles into your cloud strategy from the initial design phase.
- Consider Data Residency and Sovereignty Requirements: Pay close attention to data location requirements and jurisdictional limitations.
- Engage with Local Data Protection Authorities: Consult with relevant authorities to ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Implement Privacy by Design Principles: Proactively build privacy protections into your cloud systems and processes.
- Plan for Cross-Border Data Transfer Mechanisms: Establish clear procedures and legal frameworks for transferring data across borders.
The ENISA Cloud Security Framework provides a robust and comprehensive approach to managing cloud security risks within the complex EU regulatory environment. While it may require significant investment in implementation, its benefits, especially for organizations dealing with sensitive data or operating within the EU, are substantial. For startups and enterprises alike, understanding and applying these principles is crucial for establishing a secure and compliant cloud presence.
8. COBIT 2019 for Cloud Governance
In today’s interconnected world, robust cloud security standards are paramount, especially for businesses operating in the IN region. Among these standards, COBIT 2019 (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) stands out as a comprehensive framework for governing and managing cloud computing within enterprise IT environments. Its inclusion in this list of top cloud security standards is justified by its holistic approach, strong business alignment, and proven track record in establishing effective IT governance and management, including for cloud services. This makes it particularly relevant for startups, enterprises, cloud architects, and business decision-makers alike.
COBIT 2019 goes beyond mere technical security measures. It provides a comprehensive set of 40 governance and management objectives that address various aspects of IT, including cloud adoption and usage. This framework helps organizations align their IT strategy with business goals, manage risks effectively, and optimize resources. For organizations utilizing cloud services, COBIT 2019 offers cloud-specific design factors and focus areas, ensuring that cloud implementations are governed effectively and securely. It addresses key concerns like data security, compliance, and service availability, making it an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of the cloud landscape.
How COBIT 2019 Works for Cloud Governance:
COBIT 2019 operates on the principle of aligning IT with business goals. It provides a structured approach to defining governance processes, managing IT resources, and measuring performance. The framework is based on six governance system principles: Provide Stakeholder Value; Holistic Approach; Dynamic Governance System; Governance Distinct from Management; Tailored to Enterprise Needs; and End-to-End Governance System. These principles guide the design, implementation, and monitoring of IT governance within an organization.
Specifically for cloud environments, COBIT 2019 addresses design factors like cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), deployment models (public, private, hybrid), and the shared responsibility model. It emphasizes aligning cloud usage with business needs and managing risks associated with cloud adoption, such as data breaches, vendor lock-in, and regulatory compliance.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several organizations across various sectors have successfully leveraged COBIT 2019 for cloud governance. Large enterprises implementing cloud governance programs have used COBIT to establish a clear framework for managing their cloud environments, ensuring security and compliance. Financial institutions, with their stringent regulatory requirements, have utilized COBIT to manage cloud risks effectively. Government agencies, entrusted with sensitive citizen data, have implemented COBIT to establish robust cloud oversight. Similarly, IT service providers have used COBIT to improve service delivery and maintain high standards of security and reliability in their cloud offerings. Even multinational corporations benefit from COBIT by standardizing IT governance across their global operations, including their cloud deployments.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start with Governance System Design Factors: Analyze your organization’s specific needs and context before implementing COBIT. Consider the size and complexity of your organization, the type of cloud services you utilize, and your industry-specific regulations.
- Focus on Business Alignment and Stakeholder Needs: Ensure that your cloud governance strategy aligns with your overall business objectives and addresses the needs of all stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulators.
- Use the Capability Maturity Model for Assessment: COBIT provides a capability maturity model to assess your organization’s current governance capabilities and identify areas for improvement. This helps prioritize implementation efforts.
- Integrate with Existing Governance Frameworks: COBIT is designed to integrate seamlessly with other frameworks and standards, such as ITIL and ISO 27001. Leverage existing frameworks to streamline implementation and avoid duplication of effort.
- Leverage COBIT Toolkit and Resources: ISACA provides a wealth of resources, including toolkits, templates, and training materials, to support COBIT implementation. Utilize these resources to accelerate your implementation journey.
- Consider Professional Training and Certification: Investing in professional training and certification for your team can significantly enhance your organization’s ability to implement and manage COBIT effectively.
Pros and Cons of COBIT 2019:
Pros: Comprehensive enterprise IT governance approach, strong business alignment focus, industry-neutral and globally applicable, integrates with other frameworks and standards, mature methodology with extensive guidance, focus on value creation and risk optimization.
Cons: Complex framework requiring significant expertise, can be overwhelming for smaller organizations, implementation requires substantial resource commitment, may be too broad for highly specific cloud security needs.
While COBIT 2019 can be complex and resource-intensive, its comprehensive approach and strong focus on business alignment make it a valuable asset for organizations seeking to establish robust cloud governance. By following the tips provided and leveraging the available resources, organizations of all sizes, including those in the IN region, can effectively implement COBIT 2019 and strengthen their cloud security posture. More information can be found on the ISACA website (www.isaca.org).
Cloud Security Standards Comparison
| Standard | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27017:2015 | High – complex and resource-intensive | Significant expertise and time | Robust cloud-specific security control adherence | Cloud providers and customers managing shared responsibilities | Internationally recognized, comprehensive cloud focus |
| CSA Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) | Medium to High – comprehensive and detailed | Requires expertise but free and open | Broad security framework adoption with automation options | Cloud security assessments, compliance mapping | Industry-developed, regularly updated, multi-framework alignment |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 | Medium – flexible, abstract framework | Moderate; adaptable to organization size | Improved enterprise risk management and cybersecurity posture | Broad industry and government risk management | Widely adopted, risk-based, flexible and free |
| SOC 2 | High – thorough audit and documentation | Expensive audits and continuous monitoring | Verified operational security and customer data protection | Service organizations handling sensitive data | Builds customer trust, competitive advantage |
| FedRAMP | Very High – extremely rigorous and complex | Very high cost, long timelines, expert consultants | Federal authorization and continuous monitoring | U.S. federal cloud service providers | Government-mandated, reuse of authorization, rigorous |
| PCI DSS Cloud Security Guidelines | High – stringent compliance mandates | Intensive validation, ongoing audits | Strong payment card data protection and compliance | Organizations handling payment card data | Mandatory for payment data, strong data protection |
| ENISA Cloud Security Framework | Medium to High – EU-focused, regulatory | Moderate to high due to GDPR and regulations | Compliance with EU regulations and risk management | EU organizations, GDPR compliance | EU-tailored, privacy-focused, regulatory backed |
| COBIT 2019 for Cloud Governance | High – complex enterprise IT governance | Significant expertise and resources | Effective IT governance aligned with business goals | Large enterprises, cloud governance programs | Comprehensive governance, business alignment |
Solidifying Your Cloud Security Strategy
Navigating the complex landscape of cloud security can feel overwhelming, but adhering to established cloud security standards provides a robust framework for protecting your valuable data and infrastructure. This article explored eight key standards, from the internationally recognized ISO/IEC 27017 and CSA CCM to the rigorous requirements of SOC 2 and FedRAMP. We also touched upon NIST CSF 2.0, PCI DSS Cloud Security Guidelines, ENISA’s framework, and COBIT 2019 for governance – each offering unique perspectives and controls for specific needs and compliance obligations. Mastering these cloud security standards empowers organizations, from startups in the IN region to global enterprises, to build a layered security posture that mitigates risks, strengthens compliance, and fosters trust among stakeholders.
The most important takeaway is that effective cloud security isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Choosing the right combination of cloud security standards, tailored to your specific business objectives and risk tolerance, is crucial for long-term success. By proactively addressing these considerations, you lay the foundation for a secure, scalable, and compliant cloud environment that supports innovation and growth. Embracing these standards isn’t just a best practice – it’s a strategic imperative in today’s interconnected world.
Ready to fortify your cloud security posture and ensure compliance with relevant cloud security standards? Signiance Technologies specializes in helping organizations navigate the complexities of cloud security, offering tailored solutions based on industry best practices and these crucial standards. Visit Signiance Technologies to learn how we can empower your cloud journey with robust and comprehensive security solutions.
